atom08:FABRICATION AND ASSEMBLY LOGIC
Contents |
OPTIONS
ZERO(0) CONDITION
It is the initial condition where everything is stable and we organize the position for its use.Parameters for use organization are the density,the noise, the autonomy or the tendency to interact with other uses.The uses can move in 3 levels, ground level, first level, second level.(the height of the level is arranged according to the site and the surroundings)
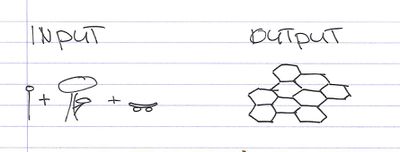
INPUT. Parameters
Uses: bike, walk, skate, relax, etc.
Connections: site entrances,trees,environment etc.
OUTPUT. Static cells
Different assembly of cellgroups possible for different sites.
WHICH ARE THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS?(according to the architectural scenario)
- maximum-minimun height of the construction
- climate
- dimensions
- can some use no included in the design
CHOISE OF THE CELL
HONEYCOMB:The honeycomb expresses the idea of economy. The hexagon has the minimal perimeter per piece area,while it uses the least material to create a lattice of cell with a given volume.
1st CONDITION
The overall shape of the structure is adapted to the size of the size. The uses are in fixed condition. The parameters (environmental) differentiate the quality of the cell. The cell can be open/close/semi-closed, in different sizes, a second material is adapted to the cell.
INPUT. Parameters
Environmental: sun, wind, rain, sound, etc.
Parameters collected live using sensors and detectors.
OUTPUT. Dynamic cells
The input gives the cells there function.
Functions: move, open, rotate, etc.
ITERATIONS
The aim is to design a non-fixed shape and to concentrate on creating an iterative system which can evolve-in changes in structural requirements, scope, and existing conditions.
SYSTEM RULES
DIFFERNTIATED GROWTH
MATERIAL
ASSEMBLY LOGIC
Design for assembly (DFA) is a process by which products are designed with ease of assembly in mind. If a product contains fewer parts it will take less time to assemble, thereby reducing assembly costs. In addition, if the parts are provided with features which make it easier to grasp, move, orient and insert them, this will also reduce assembly time and assembly costs. The reduction of the number of parts in an assembly has the added benefit of generally reducing the total cost of parts in the assembly. This is usually where the major cost benefits of the application of design for assembly occur. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Design_for_assembly