project D:Psychoacoustics
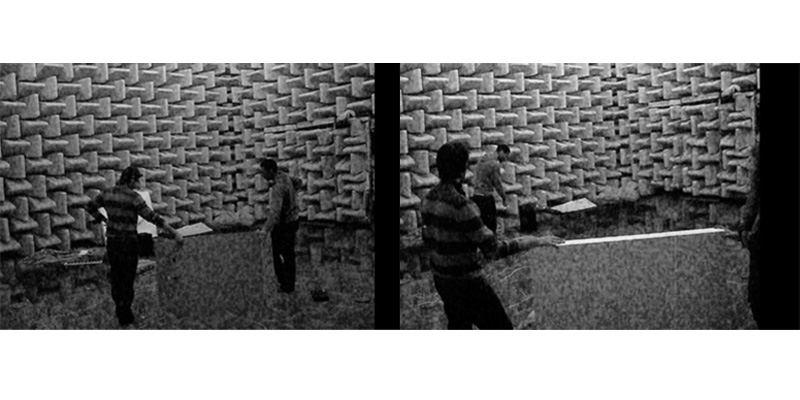
anechoic chamber characteristics
surface performance in anechoic chamber
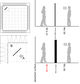
The purpose for second visit to the chamber was the testing of different materials and surface positioning in an isolated environment. The chamber is 10 cubic metres; the experiment had the intention of understanding differences between performance of surfaces and materials in the middle and corners,however it became rapidly obvious that experiments in the middle require much larger surfaces than those used, even in this isolated condition.
Attention was focused then on the corner situation, which applies to a large majority of the intervention design of intimate areas.
The first noticeable instance was the difference of absorption between the 6mm MDF board and the much thicker 150mm foam. The difference in drop is sound pressure at the source and behind the MDF panel was of 5.2 db, which is considerable noticeable to the human ear, on the contrary the thicker foam only dropped .5 db, and provided no perceivable difference.
We concluded the crucial role of density in the material, proving that thinner surfaces can be more effective in absorption than thicker and heavier ones.